GERD – Symptoms, Causes, Risks, Complications, Diagnosis & Treatment

Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease or commonly known as GERD, is a digestive disorder that effects the Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES), esophagus and stomach. Esophagus is a hollow tube that carries food we eat from our mouth to the stomach and at the end of esophagus; there is a ring of muscles called Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) which prevents the acidic stomach to leak back into esophagus. When this muscle becomes weak or not closes properly then the stomach acid leak back into esophagus and this action is called Acid Reflux. It causes irritation and inflammation to the lining of esophagus and the chronic, more severe form of Acid Reflux is GERD. It is diagnosed when acid reflux happens twice a week or has prolonged for more than two weeks. Heartburn or acidic indigestion is the most common symptom of Acid Reflux and GERD. Majority of people can control the symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease with diet, certain lifestyle changes and medications but some patients may require strong medications and even surgery for GERD treatment.
Read on further to know more about symptoms, causes, risk factors, complications, diagnosis and treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease:
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF GERD?
COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF THE CONDITION INCLUDE:
- Heartburn or acid indigestion, which is a burning chest pain, begins behind the breastbone and moving upwards to neck and throat. You may feel like food is coming back into mouth with an acid or sour taste.
- Chest pain
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Continuous dry coughing
- Sore throat
- Asthma
- Bad breath
- Damage to your tooth enamel due to acidic contents
- Feeling like a lump in your throat
If you start experiencing these symptoms with much severity or frequency then immediately make an appointment with the doctor.

WHAT CAUSES GERD?
ACID REFLUX IS THE MOST COMMON CAUSE OF THE DISEASE. SOME OTHER CAUSES INCLUDE:
- Obesity that puts an extra pressure on stomach
- Hiatal Hernia, which weakens LES and reduces pressure (We will discuss in detail about this condition in our upcoming posts)
- Smoking and alcohol
- Pregnancy also play role in GERD symptoms
- Medicines that weaken LES, such as antihistamines, antidepressants, pain-relieving medicines, calcium channel blockers and sedatives
ARE THERE ANY CONDITIONS THAT INCREASE THE RISK OF DEVELOPING GERD?
Yes, there are certain conditions that can increase the risk of developing the disease and these conditions are obesity, Hiatal Hernia, pregnancy, smoking, Diabetes, Asthma, delayed stomach emptying and connective tissue disorders.
WHAT COMPLICATIONS OCCUR DUE TO LONG-TERM GERD?
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE MAY RESULTS IN SERIOUS COMPLICATIONS IF CHRONIC ACID REFLUX PERSISTS, WHICH INCLUDES:
- Esophagitis: As a result of too much stomach acid, the lining of esophagus becomes inflamed. It may also cause Esophageal Ulcer in which sores and ulcers develop in lining of esophagus and they can bleed, cause pain and create difficulty in swallowing.
- Esophageal Stricture: The scar tissue develops in the lining of esophagus due to the damage to the cells in the lower esophagus from continuous exposure to stomach acid. This scar tissue narrows the wall of esophagus which results in difficulty in swallowing.
- Barrette’s Esophagus & Esophageal Cancer: When the normal tissue in esophagus lining abnormally replaced with different tissue that is similar to the tissue lining the stomach then the condition is called Barrett’s Esophagus. This condition, if remains untreated, may further increase the risk of Esophageal Cancer.
HOW IS GERD DIAGNOSED?
At first, the doctor will diagnose Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease based on the description of your symptoms, frequency and severity of the heartburn. The doctor may also suggest you some other tests to rule out the other possible causes of the symptoms.

WHEN GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE IS SUSPECTED OR KNOWN THEN THE DOCTOR PERFORMS THREE MAJOR TESTS OR EXAMS, WHICH INCLUDES:
- Esophageal PH monitoring: In this test, the doctor measures the amount of acid in esophagus for over a time period of 24-48 hours. This test is also used to rule out the disease if there are no symptoms of Acid Reflux.
- Upper GI Endoscopy: During this procedure, a long flexible tube with a light and camera called Endoscope is used to examine the esophagus. The doctor inserts Endoscope from your mouth which passes through the throat into the esophagus. Endoscopy is used to examine the conditions of Esophagitis (inflammation of esophagus), Stricture (narrowing of esophagus) and Barrett’s Esophagus (abnormality in tissue lining of esophagus). If your symptoms are mild then Endoscopy is usually not done but if they are severe, prolonger and didn’t respond to medication and lifestyle changes then doctor will perform Endoscopy.
- Manometry: This test is used to identify movement and pressure of valve in esophagus and allowing doctors to study the function of LES.
HOW IS GERD TREATED?
The treatment for GERD focuses on reducing the amount of acid producing in the stomach and reducing the occurrence of Acid Reflux. If you are experiencing mild symptoms then they can be treated with over-the-counter (OCT) medications and certain lifestyle changes. If you don’t get relief within few weeks and symptoms have become severe then doctor may recommend some other treatment options such as prescription-strength medications and surgery.
LET’S SEE HOW THESE TREATMENT OPTIONS HELP YOU TO TREAT GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE:
OVER-THE-COUNTER MEDICATIONS:
- Antacids neutralize the stomach acid and may provide you a quick relief, but they wouldn’t heal an inflamed esophagus due to acidic contents. Overuse of some antacids may cause constipation or diarrhea so doctor’s recommendation is necessary before taking them.
- Medications that reduce production of stomach acid are called H-2-receptor blockers. They provide long-term relief and decrease the stomach acid production for up to 12 hours.
- Proton pump inhibitors are medications that block the stomach acid production and heal the damaged esophagus. They are much stronger blockers than H-2-receptor blockers and they give time to esophagus tissues to heal.
Make sure to consult the doctor and get his/her recommendations before taking any of these medications.
PRESCRIPTION-STRENGTH MEDICATIONS:
IF YOUR HEARTBURN AND OTHER SYMPTOMS STILL PERSIST AND YOU DON’T GET RELIEF WITH INITIAL OCT MEDICATIONS THEN THE DOCTOR MAY RECOMMEND PRESCRIPTION-STRENGTH MEDICATIONS. THESE INCLUDE:
- Prescription-strength H-2-receptor blockers
- Prescription-strength proton pump inhibitors
- Medications that strengthen LES
SURGERY AND OTHER PROCEDURES:
If the condition couldn’t be able to control through OCT and prescription-strength medications then the doctor recommends surgery in order to avoid more damage to esophagus and stomach. It includes:
Nissen Fundoplication: During this surgery, the LES is tightened by wrapping the top of stomach portion around the outside of the lower esophagus. It reinforces the LES while preventing the Acid Reflux.
Linx Surgery: It is the latest treatment for GERD approved by FDA, in which a device called Linx, which is an expandable ring of metal beads, is wrapped around the junction of esophagus and stomach. It keeps the stomach acid to reflux back into the esophagus and at the same time it allows food to pass into the stomach.
LIFESTYLE AND DIETARY CHANGES:
HERE ARE SOME OF THE SUGGESTED LIFESTYLE AND DIETARY CHANGES THAT CAN REDUCE HEARTBURN AND OTHER SYMPTOMS:
- Avoid foods and drinks that weaken the LES and trigger the heartburn such as fatty foods, chocolate, peppermint, coffee and alcoholic beverages. Avoid those foods that you know trigger your heartburn.
- Maintain a healthy weight by regular exercising and if you are obese then slowly reduce your weight. You can ask the doctor to devise a weight loss plan for you.
- Eat smaller meals while avoiding overeating.
- Don’t lie down or go to bed for at least 3 hours after eating a meal.
- If you experience heartburn at night or while sleeping then elevate the head of your bed by putting wood or cement blocks under the feet of the bed so that the head is raised by 6-9 inches.
- Avoid smoking because it affects the function of LES.
- Avoid wearing tight-fitting clothes especially around your waist which puts pressure on your abdomen and LES.
EXPERIENCING GERD SYMPTOMS, CONSULT SPECIALISTS AT GI ENDOSCOPY PRACTICE:
We know that Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease can limit the daily activities and productivity but it is rarely life-threatening disease. Most of the people will find relief with understanding of the actual causes and proper treatment plan that GI Endoscopy Practice physicians are providing to the patients experiencing the problem. If you’re facing the problem of heartburn or other possible symptoms then consult our board certified, capable, experienced, trained and highly recommended physicians in NJ. You will get personalized care and a best GERD treatment plan paving a way for a healthy life.
You Might Also Enjoy...


What Is The Natural Treatment For H. Pylori Infection?
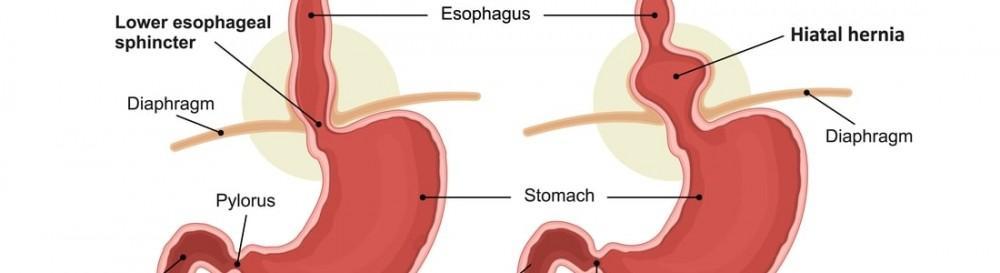
A Complete Overview of Hiatal Hernia

Constipation – How To Use The Best 5 Essential Oils?

How The Procedure Of Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Is Performed