Colonoscopy – Reasons, Prep, Procedure, Results, Risks

Prolonged constipation, bleeding lesions from anus, pain in lower tummy, persistent diarrhea, and change in your bowel habits might be linked with the problems in your large intestine or colon. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms continuously or you feel that they are worsening then you should consult your physician immediately as these can be due to some serious colon diseases. Colonoscopy is normally the first procedure that your physician recommends as this medical exam is most commonly used to assess your colon or large intestine. New Jersey medical board also recommends this exam because it greatly helps in the early diagnosis of some of the serious diseases of large intestine. A workable treatment plan that gives best results depends on the timely diagnosis of the problem which makes it essential to consult a physician as soon as the above mentioned symptoms occur.
AN OVERVIEW OF COLONOSCOPY:
Here we give you a brief overview of Colonoscopy procedure. This is a general guideline of the procedure; however the arrangements and ways of performing the test may vary between different physicians. You must follow the instructions given by your doctor.
WHAT IS MEANT BY COLONOSCOPY?
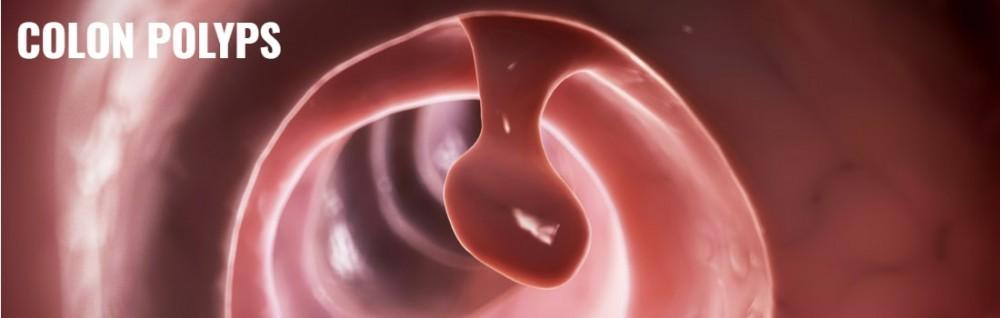
Colonoscopy is the test that is used to diagnose the problems or abnormalities in the colon and rectum. In the procedure, a long, flexible tube carrying a tiny camera on the tip is inserted into rectum to get the inside view of the entire colon. Tissue samples for biopsy can also be taken during the procedure along with the removal of abnormal tissues or polyps.
WHY IT IS PERFORMED?
The procedure is used to look for signs and symptoms of abdominal pain, constipation, bleeding, diarrhea and other intestinal problems such as Ulcerative Colitis, Crohn’s Disease, Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis. It is used as a screening test to diagnose colon cancer and to remove polyps from the colon.
HOW TO PREP FOR COLONOSCOPY?
The most important step in Colonoscopy preparation is to clean or empty the colon because any residue may hinder the view of the colon during the exam. In order to empty the colon, it is necessary to follow the instructions of the doctor which may consist of a special diet plan a day before exam, using laxative a night before procedure, using an enema kit and adjusting routine medications.
HOW THE PROCEDURE IS PERFORMED?
Doctors usually give mild sedatives at the start of the procedure to avoid any discomfort and the patient will be asked to lie down on their side with knees drawn towards the chest. The Colonoscope is then inserted into the rectum and it is long and flexible enough that it can spread through the entire colon. The colonoscope comprises of three channels: a torch light channel, a multipurpose tube and a tiny video camera channel that sends images to the monitor from where doctor can view the colon. Air is pumped through the multipurpose tube to dilate the colon and various instruments can be inserted and used to collect tissue sample or to remove polyp. The complete exam takes approximately 20 – 60 minutes depending on the requirement of the procedure.
WHAT TO EXPECT AFTER THE PROCEDURE?
After the procedure, the patient may feel the need to pass gas or feel bloated but it is normal because of the air pump during the exam. It takes about an hour to recover from the effects of sedative and driving or working should be avoided as it might take 1 day to fully recover from sedative. The patient will also need to eat a special diet temporary as per doctor recommendation and might find small traces of blood in the first bowel movement. If you continue to get blood or blood clots with abdominal pain please consult your doctor.
WHAT ARE THE RESULTS OF THE PROCEDURE?
The doctor will review the results of the procedure and then devise the way forward. The results can either be positive or negative. If the doctor does not find any problem or abnormality in colon then Colonoscopy is considered as negative. If the doctor finds any abnormal tissue or polyps in the colon then Colonoscopy is considered positive. Depending on the individual condition, the doctor then devises a proper treatment plan.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS INVOLVED IN COLONOSCOPY?
There are very few risks involved in the procedure. Some rare complications include adverse reaction to sedative, bleeding from the site from where tissue sample is taken or polyp is removed and a tear in lining of colon or rectum. The sign of bleeding might require hospitalization or surgery.
WHAT TO THINK ABOUT?
Pregnant women should not go for this exam unless there is no alternative. People with the age of 50 or over have high risk of colon cancer and that is why doctors recommend routine Colonoscopy for elderly ones. There are also other screening tests available for problems in the colon. Always talk to your doctor about your preferences, risks involved and the best procedure.
You Might Also Enjoy...


What Is The Natural Treatment For H. Pylori Infection?
A Complete Overview of Hiatal Hernia

Constipation – How To Use The Best 5 Essential Oils?

How The Procedure Of Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Is Performed