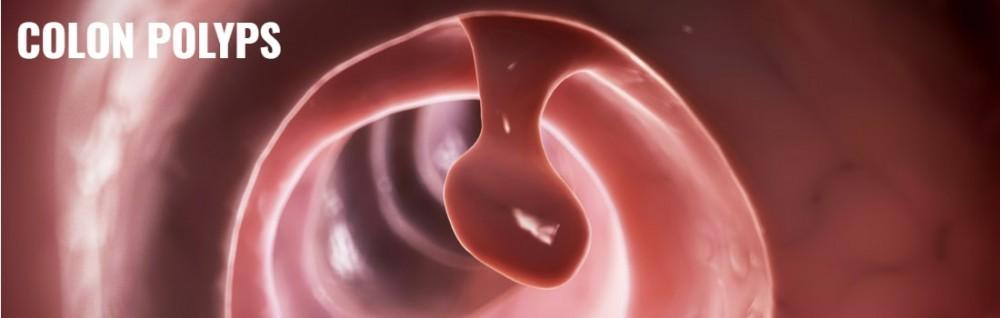
Colon Cancer – Overview & Facts
The cancer of the large intestine or colon is called as Colon Cancer. The cancer of last few inches of colon is called as Rectal Cancer. Both these conditions together referred as Colorectal Cancer. The Colon Cancer starts with small non-cancerous polyps that develop in colon. These polyps further become Colon Cancer, if not diagnosed early and treated properly. As these polyps produce few or no symptoms so it is highly recommended to have regular screening exams to diagnose and remove polyps before they become Colon Cancer. The early detection of polyps and appropriate treatment is imperative to cure the Cancer of Colon. Below is a brief overview of Colon Cancer: its symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment.
SYMPTOMS OF COLON CANCER:
The major sign and symptom is the visible change in bowel movements such as constipation, diarrhea, and changes in stool’s consistency lasting more than 4 weeks. Rectal bleeding or blood in the stool is another symptom. Some other common signs are gas, cramps, abdominal pain, fatigue, frequent weight loss and a sense of feeling that bowel is not empty completely. Majority of patients didn’t face any symptoms at early stage of the disease but the symptoms start appearing at later stage. These symptoms may vary from patient to patient depending on the size of cancer and its location in the colon. The patient must consult the doctor if he/she experiences any of these symptoms.
CAUSES OF COLON CANCER:
The actual cause of Colon Cancer is still unknown. It is known to doctors that the condition occurs when the DNA of healthy cells in the Colon gets damaged. Healthy cells grow and divide for the normal functioning of human body. If the DNA of these cells damaged or become cancerous then they continue to grow and divide even it isn’t required. They start accumulating and form tumors. Eventually, these tumors start affecting nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
RISK FACTORS FOR COLON CANCER:
- The factors that increase the risk of developing the disease include:
- The disease commonly occurs in elderly people over the age of 50.
- The people belongs to African-American race may have high risk of developing the condition.
- Family history is the major risk factor. The risk even becomes higher if more than one family member suffered from the disease.
- Some genetic syndromes passed through family generations also increase the risk of developing disease.
- Some severe inflammatory diseases of colon such as Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s disease are the major risk factors.
- If a patient had Colon Cancer or cancerous Colon Polyps then the risk of developing it in future increases.
- Studies have shown that the use of diets low in fiber and high in fat or calories such as red meat and smoked meat increase the risk of the disease.
- Another risk factor associated with developing disease is Diabetes.
- People who are obese have high risk of developing the Cancer and high chances of dying from it as compared to normal weight patients.
- Smoking and use of alcohol may increase risk of the condition.
- An inactive lifestyle with no physical exercise is another risk factor.
- If a patient got radiation therapy at the abdomen to treat previous cancers then it may increase the risk of Colon Cancer.
DIAGNOSIS:
According to doctors, there are various screening tests available to diagnose the disease at an early stage. Only the early diagnosis can pave the way for preventing and curing the disease. It also reduces the risk of dying of the disease. People with average risk of disease can begin the screening tests after 50. On the other hand, people with high risk must consider for the tests sooner. The doctor can better recommend an appropriate screening test to the patient.
The most common screening test used to diagnose the disease is Colonoscopy. In this procedure, a colonoscope is used to examine the entire Colon. If the doctor founds any Polyp then it can be removed right at the spot. A tissue sample (biopsy) taken during the procedure is also used for diagnosis.
Although a blood test doesn’t actually diagnose the Cancer, a doctor can get a clear picture of a patient’s overall health such as proper functioning of major parts of the body.
TREATMENT FOR COLON CANCER:
The type of treatment option that is suitable for a patient depends largely on the stage of Cancer. The doctor recommends proper treatment option according to each patient’s condition. The common three treatment options are surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Below is a brief overview of each option:
Surgery:
There are different ways of surgery depending on the stage of Cancer; early stage surgery, invasive stage surgery and advanced stage surgery. The early stage surgery includes removing a small cancerous polyp during Colonoscopy. The invasive stage surgery includes partial colectomy, colostomy and lymph node removal. The advanced stage surgery involves an operation that relieves the blockage of colon and symptoms such as bleeding and pain. All these ways of surgeries may recommend by the doctor according to individual patient’s condition.
CHEMOTHERAPY:
In this therapy, drugs are used to destroy cancerous cells. Chemotherapy for Colon Cancer may be given after surgery reducing the recurrence of disease. It may be given before surgery to shrink cancerous cells. This therapy is also recommended if the Cancer spreads to other parts of the body. The combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy is used to cure the Rectal Cancer.
RADIATION THERAPY:
X-Rays are used to kill the cancer cells that might have remained after the surgery, to contract large tumors before surgery and to relieve symptoms of Colorectal Cancer. Radiation is rarely used to treat early stage cancer and it usually used to treat Rectal Cancer.
Early diagnosis, regular check-ups, screening exams, tests and an appropriate treatment plan will effectively prevent and cure Colon Cancer so a patient may continue to lead a healthy life.
You Might Also Enjoy...


What Is The Natural Treatment For H. Pylori Infection?
A Complete Overview of Hiatal Hernia

Constipation – How To Use The Best 5 Essential Oils?

How The Procedure Of Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Is Performed